Inductive sensing adopted for the motorcycle APS
An inductive sensor is a sensing technology that uses electromagnetic induction to detect the position of a target (metal object).
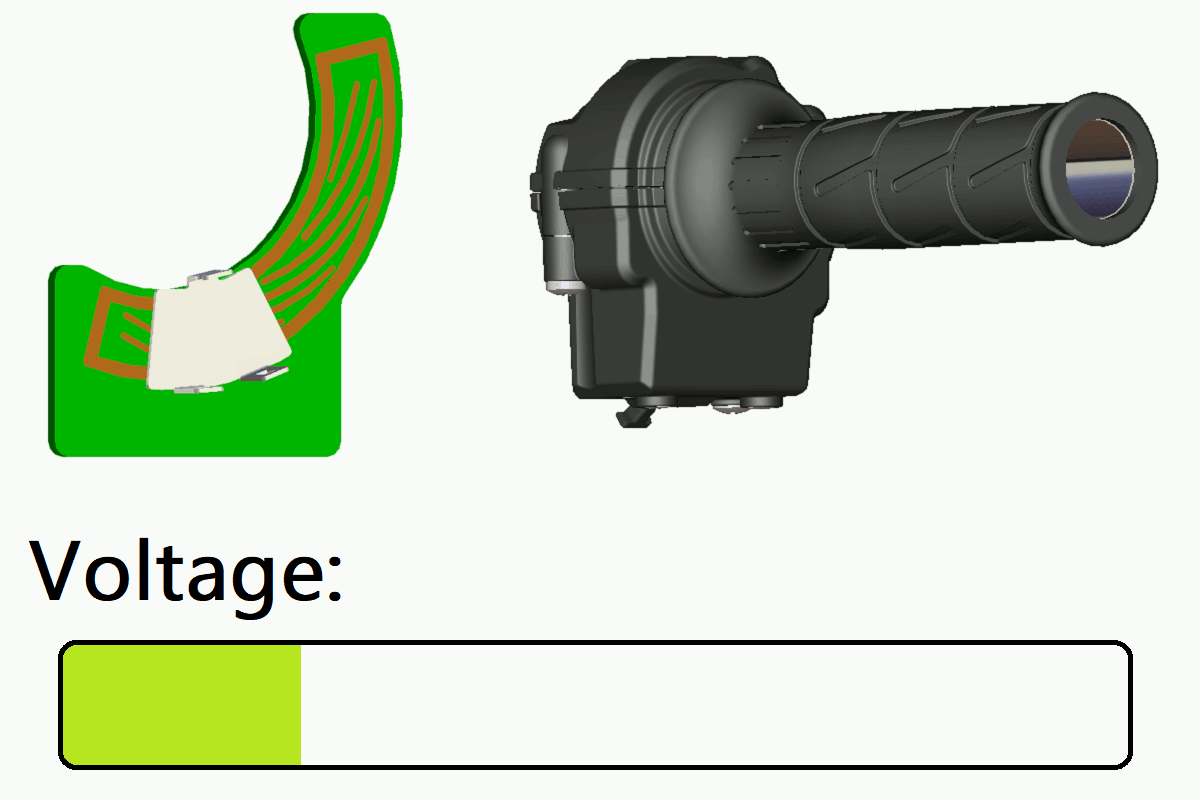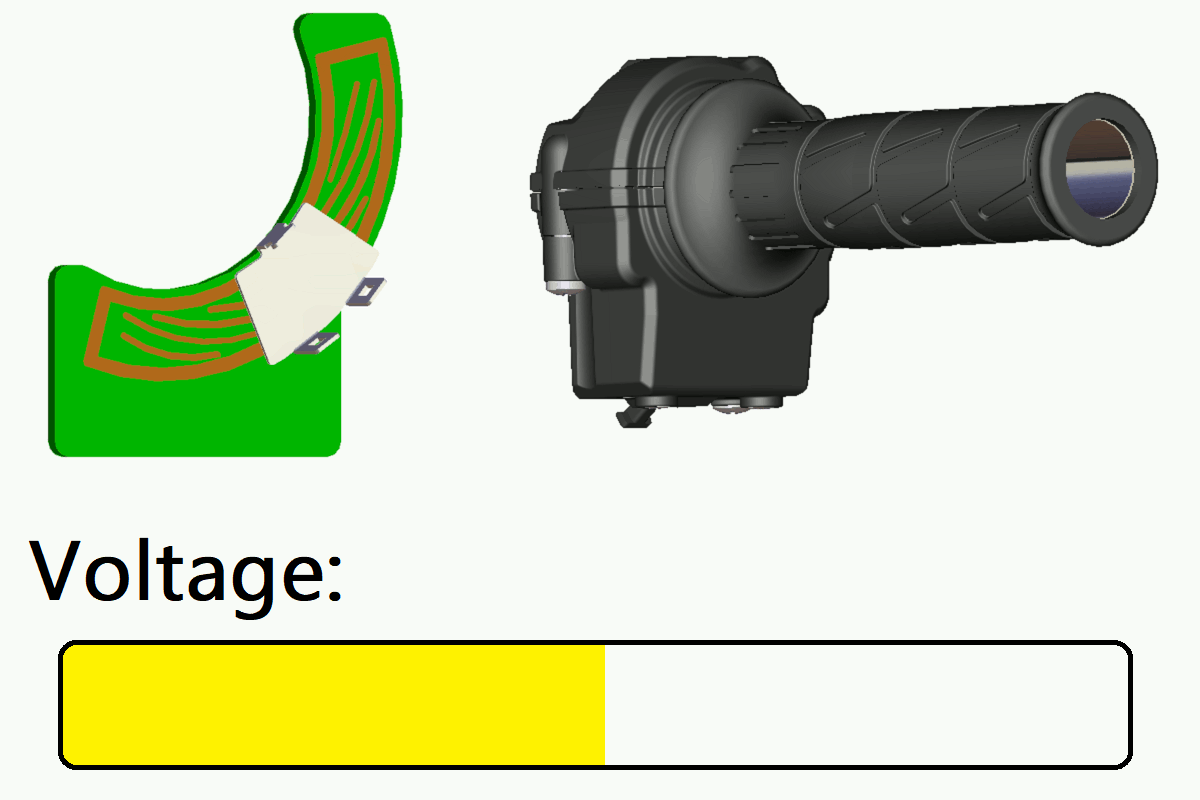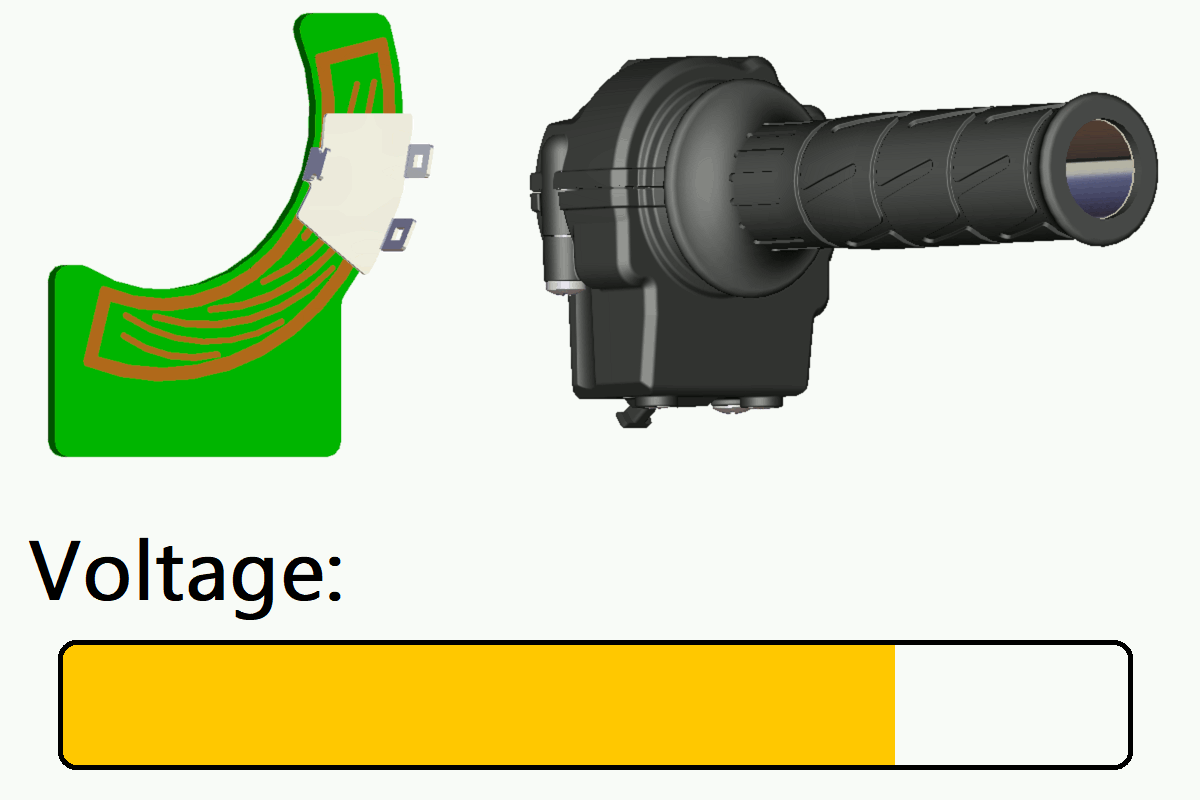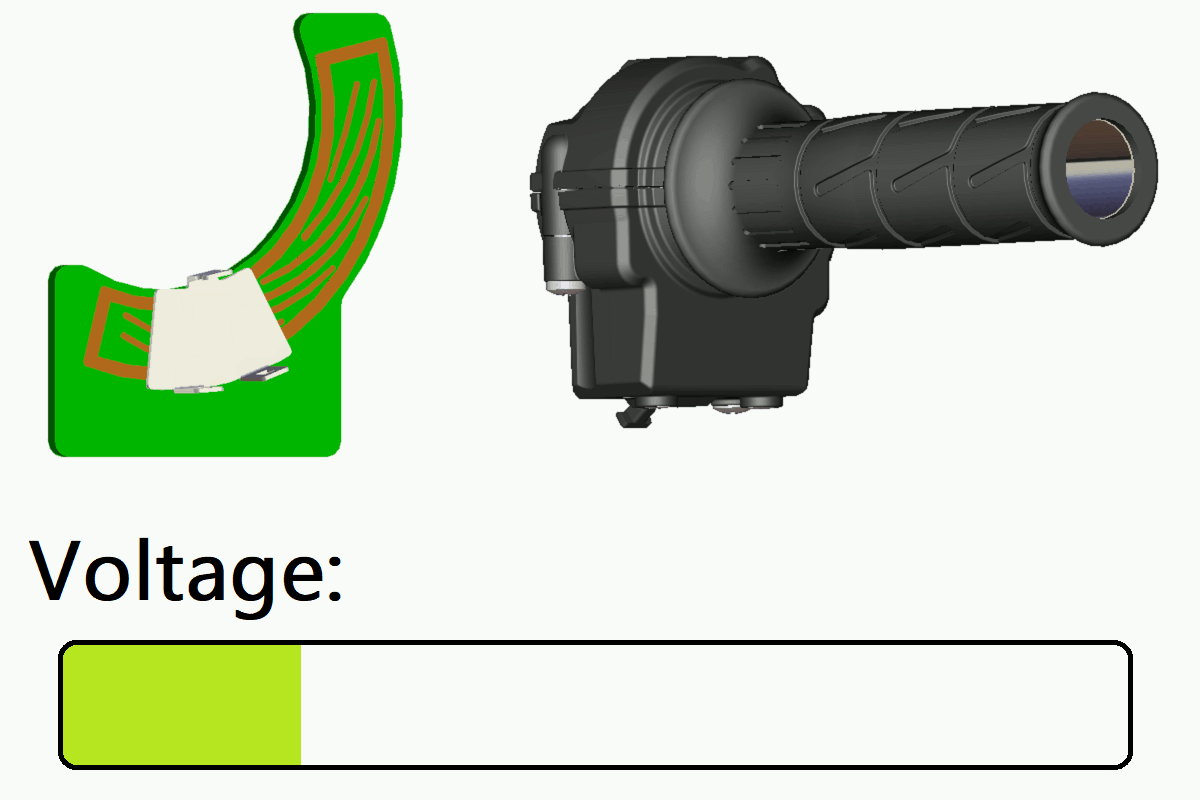
In this product, a coil pattern (sensing circuit) is formed on the printed circuit board (PCB).
When a metal target plate moves over this coil pattern as the grip is operated, it causes changes in the induced magnetic field.
The sensor detects these changes and outputs a voltage signal corresponding to the target position. This enables smooth, high-precision throttle control.
Conventional magnetic APS (accelerator position sensors) detect rotation angle using a magnet combined with a Hall-effect IC.
However, magnets often rely on rare-earth elements, which pose supply risks due to geographically concentrated production and
environmental impacts from mining and refining.1
Our product adopts an inductive sensing method that uses changes in the induced magnetic field (electromagnetic induction). As a result, it uses no magnets and can be produced without rare earths. This approach achieves both lower environmental impact and a more stable supply chain.
Asahi Denso has long developed and produced a wide range of magnetic-sensor APS units.
Our new inductive APS uses a different structure and detection principle, yet draws on our APS design expertise to deliver the same familiar operating feel and responsiveness as our previous models-finished as a next-generation APS powered by a new sensing technology.
![Asahi Denso Co., Ltd. | The special maker for Human and Machine Interface [Open the way]](/uploads/op-asahidenso/en-logo.png)